India’s First Case of Mpox Clade 1b Variant Reported: Know What is Mpox and How Dangerous is It
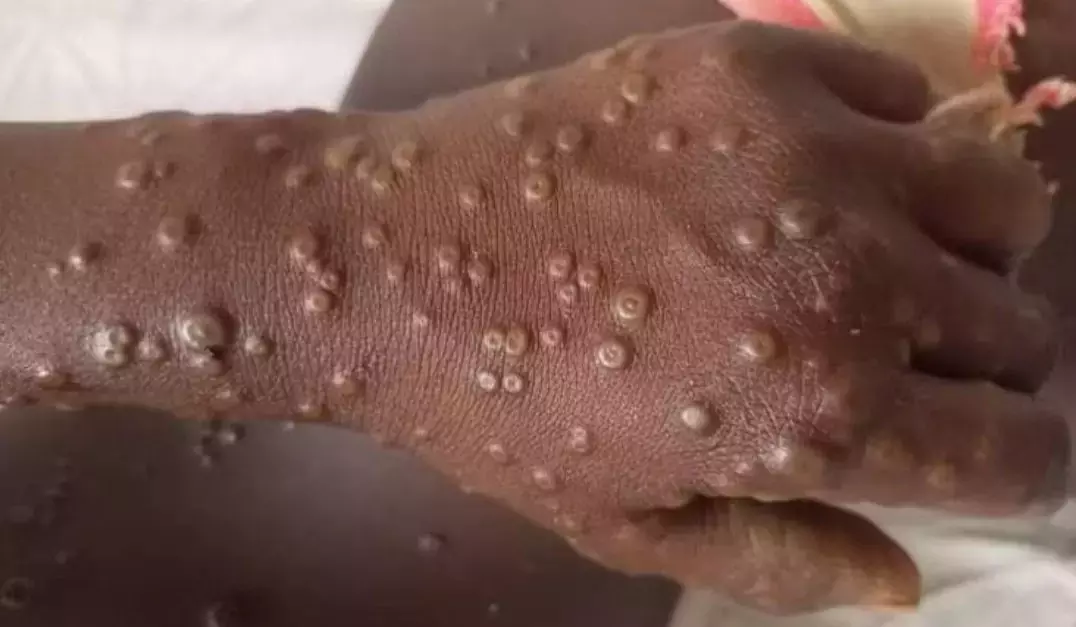
A patient of the deadly clade 1b variant of Mpox has been confirmed in India. The case was reported in Kerala's Malappuram district, where the deadly variant was identified in a 38-year-old man who had recently returned from the United Arab Emirates.
Government sources said, "This is the country's first Mpox clade 1b case. The man had a fever and chickenpox-like rashes, after which doctors suspected him and his sample was sent for testing." This is the second case of Mpox in India. The first case was reported in Delhi, but that case was of clade-2, which was different from the WHO public emergency. The recent case is related to this warning of WHO.
Mpox clade 1b spreads rapidly. According to the World Health Organization, it spreads especially through sexual networks and the virus has become a major crisis in the neighboring countries of the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). Mpox was earlier known as monkeypox, but WHO changed its name. This virus has long been a major health problem in African countries.
What is Mpox?
Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, is a viral disease caused by the monkeypox virus, a species of the Orthopoxvirus genus. There are two distinct clades of the virus: clade-1 (with subclades 1a and 1b) and clade-2 (with subclades 2a and 2b). A global outbreak of Mpox caused by clade 2b strains occurred in 2022-2023.
Mpox remains a threat today, and a surge in cases in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and other countries caused by clades 1a and 1b has raised concern.
Vaccines are also available for Mpox. Vaccination should be considered along with other public health interventions.
Common symptoms of Mpox are skin rash or mucosal lesions that may last for 2-4 weeks and may also be accompanied by fever, headache, muscle aches, back pain, low energy, and swollen lymph nodes.
How can Mpox be spread?
Mpox can be spread through close contact with someone who has Mpox, with contaminated materials, or with infected animals. During pregnancy, the virus can be spread to the fetus, or the newborn during or after birth. Mpox is treated with supportive care for symptoms such as pain and fever, with close attention to nutrition, hydration, skin care, prevention of secondary infections, and treatment of co-infections, including HIV.
According to the World Health Organization, since January 1, 2022, cases of Mpox have been reported in 121 member countries. This information has been given in the WHO report and it has been told that 102,997 cases have been confirmed worldwide. Apart from these, 223 deaths have also been recorded. In July alone this year, 1,425 cases and six deaths were recorded.
55 percent of Mpox cases were reported in African countries. Apart from these, 24 percent of the patients of this case were identified in the American regions and 11 percent of the cases have been reported in Europe. The Southeast Asia Region (SEAR) has reported 1 percent of the total cases. Hospitals and labs have been set up in India to deal with its problems.
